




Unidata IDV Workshop for version 7.0u1 > Advanced Topics > Scripting with IDV

4.3.5 Interactive Scripting with the IDV and the Jython Shell
IDV Jython scripting environment to visualize data interactively.
Leveraging the IDV Jython command shell with VisAD creates a powerful combination for scripting IDV workflows as well as "experimental exploration" of data and the IDV and VisAD APIs. In this section, we will examine to how make use of the IDV Jython scripting environment to visualize data interactively.
To achieve this objective, we will leverage the VisAD Jython APIs. Complete documentation for these APIs can be found here:
The JPython (the old name for Jython) VisAD API is a low-level API for interacting with VisAD objects from the Jython environment. The IDV JythonLib is a higher-level API built on top on the VisAD JPython API. In the following exercises we will be using both these APIs.
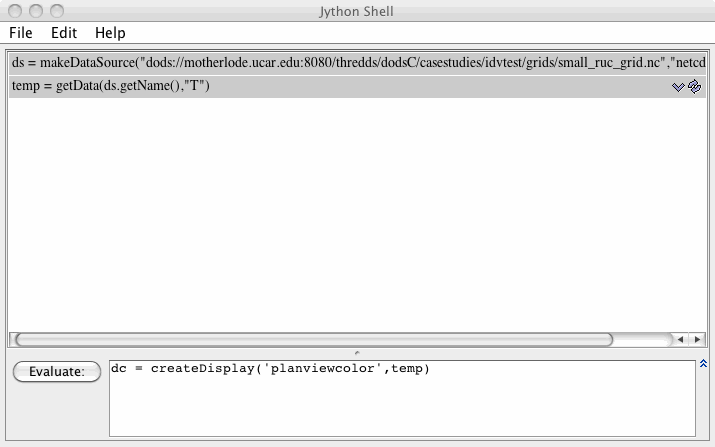
These exercises are meant to be done in sequence. We will be using the Jython interactive shell. Please enter the commands described below in the evaluation area as shown in the figure.
- If other displays and data are already loaded, select the
menu item
or the
 icon in the toolbar to clear them out.
icon in the toolbar to clear them out.
- Select the menu item.
- Write a script to load some RUC data and display it in the planview. Copy this text into the Jython Shell to the right of the evaluate button and click on the
Evaluate button.
ds = makeDataSource("dods://motherlode.ucar.edu:8080/thredds/dodsC/casestudies/idvtest/grids/small_ruc_grid.nc","netcdf.grid")
temp = getData(ds.getName(),"T")
dc = createDisplay('planviewcolor',temp)
This script should result in a color shaded plan view of temperature data.
- Have the IDV prompt the user for the data interactively.
rh = selectData()
You will be prompted for data. Select relative humidity.
dc = createDisplay('planviewcolor',rh)
- We will now write a couple of convenience methods
def retrieveData(dset, field) :
return getData(dset.getName(),field)
def createColorShadedPlanView(field) :
return createDisplay('planviewcolor',field)
- Obtain the U and V wind fields and display wind speed in plan view
u = retrieveData(ds,"u")
v = retrieveData(ds,"v")
Now invoke the windpeed formula you wrote in an earlier
showLib()
ws = windSpeed(u,v)
dc = createColorShadedPlanView(ws)
If you did not complete that exercises, here is the wind speed formula.
def windSpeed(u,v):
usqd= u*u
vsqd= v*v
ws = sqrt(usqd + vsqd)
return ws
- This is a slightly more complicated example involving the comparison and difference observational satellite temperature data with NAM model temperature data
If other displays and data are already loaded, select the
menu item
or the  icon in the toolbar to clear them out.
icon in the toolbar to clear them out.
sds = makeDataSource("/Users/chastang/tmp/sat/GOES-East100.area")
img = selectData()
gds = makeDataSource("http://motherlode.ucar.edu/thredds/dodsC/model/NCEP/NAM/CONUS_40km/conduit/NAM_CONUS_40km_conduit_20110712_1200.grib2")
grid = selectData()
Here you will be prompted for the field. Select Formulas -> Grid -> Make 2D slice, then pick the 300hPa temperature -- one time only!
diff = img - grid
createDisplay('planviewcolor',diff)
Exporting to Jython Library
As you gain familiarity with the IDV Jython Scripting environment, you will eventually wish to save and export your methods to the Jython library. For the purposes of illustrating this functionality, in this exercise, we will write a simple method and export it to the library.
- Select the menu item.
Note that it is possible to have several shell windows open at once. This is a nice feature as you develop your Jython methods in one shell, then copy / paste the completed method to the fresh shell for export.
- Let's write a formulate to calculate the dew point from the temperature, and relative humidity.
def dew_c(rh, temp_c):
from java.lang import Math
l = Math.log(rh / 100.0)
m = 17.27 * temp_c
n = temp_c + 237.3
b = (l + (m / n)) / 17.27
dew_c = (237.3 * b) / (1 - b)
return dew_c
- Select the menu item. This action will prompt you for a procedure name, but leave this field blank and click the
OK button.
- You are now in your Jython User library where you should see your method. Click the
Save button. You now have your Jython method available for later use.
The VisAD Jython shell is a full programmatic environment. We have only scratched the surface of what can be achieved. We encourage users to interactively experiment with the IDV in this manner.






Unidata IDV Workshop for version 7.0u1 > Advanced Topics > Scripting with IDV
 icon in the toolbar to clear them out.
icon in the toolbar to clear them out. icon in the toolbar to clear them out.
icon in the toolbar to clear them out.




