The preferred way to open a NetcdfFile is through the NetcdfDataset.openFile factory method:
String filename = "http://thredds.ucar.edu/thredds/dodsC/model/NCEP/GFS/CONUS_80km/GFS_CONUS_80km_20061019_0000.grib1"; NetcdfFile ncfile = null;NetcdfDataset.openFile does the follwing:
try {
ncfile = NetcdfDataset.openFile(filename, null);
process( ncfile);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log("trying to open " + filename, ioe); } finally { if (null != ncfile) try { ncfile.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { log("trying to close " + filename, ioe); } }
When you want the Netcdf-Java library to deal with missing values and scale/offset unpacking, and to identify Coordinate Systems, you should use the NetcdfDataset.openDataset factory call, for example:
String filename = "http://thredds.ucar.edu/thredds/dodsC/model/NCEP/GFS/CONUS_80km/GFS_CONUS_80km_20061019_0000.grib1"; NetcdfDataset ncd = null;Note that NetcdfDataset is a subclass of NetcdfFile, and so can be used wherever a NetcdfFile is used. NetcdfDataset.openDataset does the following:
try {
ncd = NetcdfDataset.openDataset(filename);
process( ncd);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log("trying to open " + filename, ioe); } finally { if (null != ncd) try { ncd.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { log("trying to close " + filename, ioe); } }
When you open a NetcdfDataset in enhanced mode (the default), any Variables that have the attributes scale_factor and/or add_offset are considered to be packed data Variables, whose data should be converted with the formula:
unpacked_data_value = packed_data_value * scale_factor + add_offsetusually the packed data type is byte or short, and the unpacked type is float or double, so the data type of the packed data Variable is promoted to float or double.
Missing data is indicated by the valid_min, valid_max, valid_range, missing_value or _FillValue attributes. When a Variable has any of these attributes, the VariableDS.hasMissing() method returns true. You can test for missing values with the VariableDS.isMissing( value) method.
To open a NetcdfDataset in enhanced mode, toggle the enhance button ![]() on the ToolsUI Viewer tab to
ON.
on the ToolsUI Viewer tab to
ON.
NetcdfDataset will try to identify the Coordinate Systems in the dataset by calling a CoordSystemBuilder class that knows how to interpret the Conventions for that dataset. The information is placed in Coordinate objects that follow this abstract model (see the javadoc for the specifics):
: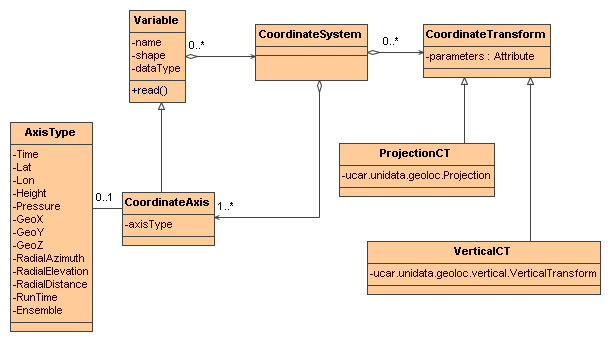
To write your Coordinate System Builder, see here. To see the list of CoordinateBuilder classes, look at the source code in the ucar.nc2.dataset.conv package.
When writing netCDF files, we recommend using the Climate and Forcast (CF) Convention if possible. When an IOSP reads in a non-netCDF file, it should choose a Convention to use to encode the Coordinate Systems.
You can use ToolsUI CoordSys Tab to view the Coordinate Systems that have been constructued. This consists of 3 tables that show the data variables, the coordinate systems, and the coordinate axes.
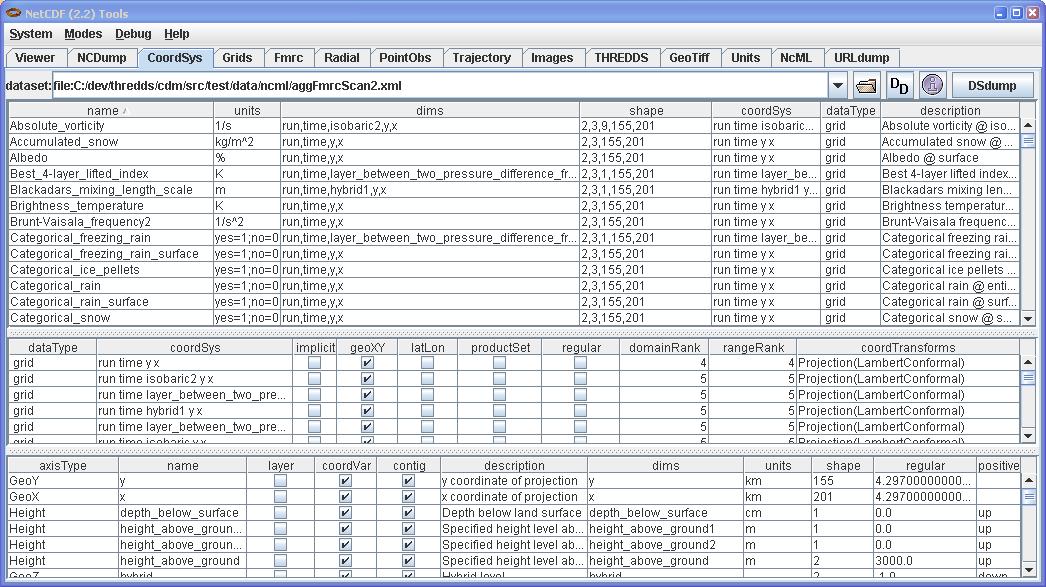
The following is applicable to version 4 of the Netcdf-Java library. Netcdf-Java version 2.2 effectively has only two enhance modes, All and None.
The kind of enhancements made when a NetcdfDataset is opened is described by NetcdfDataset.Enhance, an enumerated type with these possible values:
When using the ScaleMissing enhance mode, scale/offset/missing attributes are processed when the dataset is opened, and the datatype of a Variable is promoted if necessary to match the unpacked data type. Data is automatically converted when read.
When using the ScaleMissingDefer enhance mode, scale/offset/missing attributes are processed when the dataset is opened, but the datatype of a Variable is NOT promoted, and data is not converted. After reading data, you can convert the entire Array with VariableEnhanced.convertArray(Array data), or convert single values with the convertScaleOffsetMissing methods, eg VariableEnhanced.convertScaleOffsetMissing(byte value).
When using CoordSystems enhance mode, CoordSysBuilder is called to populate the coordinate system objects in the NetcdfDataset when the dataset is opened.
When using ConvertEnums enhance mode, Variables of type enum are promoted to String types and data is automatically converted using the EnumTypedef objectss, which are maps of the stored integer values to String values.
The enhancement of a dataset can be controlled by passing in a Set of Enhance to NetcdfDataset.openDataset(). The default enhance mode is
Set<Enhance> EnhanceAll = Collections.unmodifiableSet(EnumSet.of(Enhance.ScaleMissing, Enhance.CoordSystems, Enhance.ConvertEnums));
and can be changed through NetcdfDataset.setDefaultEnhanceMode(Set<Enhance> mode).
The simplest factory method, NetcdfDataset.openDataset( location), uses the default enhance mode. Other factory methods with a boolean enhance parameter, such as NetcdfDataset.openDataset(String location, boolean enhance, CancelTask cancelTask) use the default enhance mode if enhance is true, and EnhanceMode.None if enhance is false. Other classes, such as GridDataset, also use the default enhance mode.
The most general factory method for opening NetcdfDataset allows one to explicitly set the EnhanceMode:
NetcdfDataset openDataset(String location, Set<Enhance> enhanceMode, int buffer_size, CancelTask cancelTask, Object spiObject);
One can also set the buffer size used for reading data, pass in a CancelTask object to allow user cancelling, and pass an arbitrary object to the IOServiceProvider that handles the dataset. These last 3 parameters correspond to the ones in the similar factory method for NetcdfFile:
NetcdfFile openFile(String location, int buffer_size, CancelTask cancelTask, Object spiObject);
Advanced applications like servers might want to enable the caching of NetcdfDataset and NetcdfFile objects in memory, for performance. Caching is safe to use in a multithreaded environment such as a servlet container like Tomcat. Caching keeps resources such as file handles open, and so cache sizes should be carefully considered.
To enable caching, you must first call
NetcdfDataset.initNetcdfFileCache(int minElementsInMemory, int maxElementsInMemory, int period);
where minElementsInMemory are the number of objects to keep in the cache when cleaning up, maxElementsInMemory triggers a cleanup if the cache size goes over it, and period specifies the time in seconds to do periodic cleanups.
One then calls the acquireFile() or acquireDataset factory methods instead of openFile() and openDataset. For example:
NetcdfDataset.initNetcdfFileCache(100,200,15*60); // on application startup
...
NetcdfFile ncfile = null;
try {
ncfile = NetcdfDataset.acquireFile(location, cancelTask);
...
} finally {
if (ncfile != null) ncfile.close();
}
...
NetcdfDataset.shutdown(); // when terminating the application
Note that when done with the file, the close() method is called as usual. Instead of actually closing the file, it is left in the cache for subsequent acquiring.
Note also that calling NetcdfDataset.shutdown is crucial for terminating background threads that otherwise can prevent process termination.
 This document was last updated on July 2013
This document was last updated on July 2013