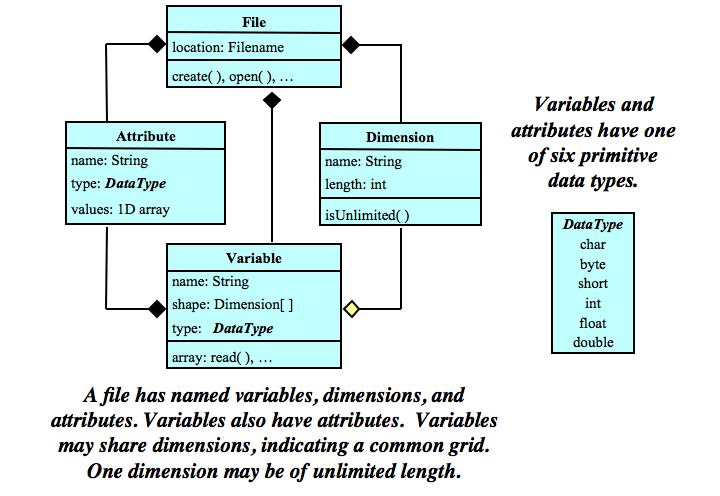
The Classic Data Model represents data sets using named variables, dimensions, and attributes. A variable is a multidimensional array whose elements are all of the same type. The shape of each variable is specified by a list of dimensions. Dimensions are named axes that have a length. Variables may share dimensions, indicating a common grid. One dimension in a dataset may be of unlimited length, so data may be efficiently appended to variables along that dimension. A variable may also have attributes, which are associated named values. Variables and attributes have one of six atomic data types: char, byte, short, int, float, or double.
A diagram of the Classic Data Model exhibits its simplicity: